Industry
Precision Power: Choosing the Right CNC Machine for Your Needs
Precision in Modern Manufacturing
Precision and speed are essential, and one can even say mandatory, to modern manufacturing sectors such as automotive, aerospace, signage, and cabinetry. The evolution from manual machining to computer-controlled CNC technology has transformed production by reducing human error, boosting efficiency, and ensuring consistent, high-quality outputs. These advancements optimise material use and enable manufacturers to meet demanding production timelines while maintaining a competitive edge.
Understanding the CNC Machine
A CNC machine is a computer-driven tool that automates the cutting, milling, or shaping of materials based on digital programming. It transforms intricate digital designs into physical components with unparalleled precision and repeatability. Capable of working metal, plastics, composites, and wood, the CNC machine is actually a prime example of the synergy between software control and mechanical precision essential in current fabrication processes.
Benefits and Why They Really Matter
It provides superior accuracy and consistency, dramatically lowering manual errors. Its ability to operate continuously with little supervision supports high-volume production and complex part manufacturing.
And that is why having your very own CNC machine can revolutionise outputs, enabling innovation and scalable, reliable manufacturing to exact specifications demanded by modern industries. This will make any process and venture more safe, secure with the reproducible results, time and time again in the long run.
Exploring Options and Choosing the Right One for You
CNC machines are diverse, including laser cutters, plasma cutters, routers, and oxy-fuel machines, each ideal for specific materials and tasks. Plasma cutters excel with thick metals; routers shine on softer substrates like wood and plastics. Choosing involves assessing production volume, workspace, precision needs, and material types.
Important specs include bed size, spindle power, cutting speed, and CAD/CAM compatibility. Emphasis on easy maintenance and software upgradability ensures longevity. Consulting experts and doing hands-on trials help avoid costly mismatches, while prioritising versatile tooling and user-friendly controls eases operational demands.
Materials and Technology Behind CNC
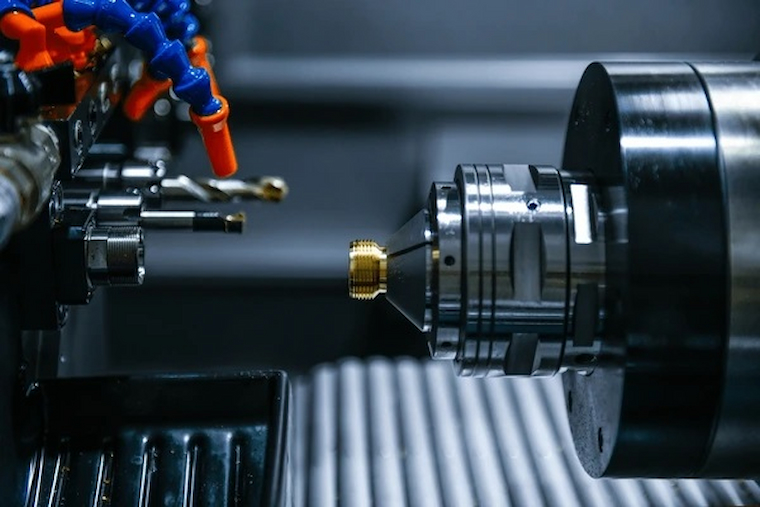
Modern ones handle mild steel, aluminium, stainless steel, brass, plastics, and composites. Tooling and machining parameters must align with material characteristics to optimise finish and efficiency. Advances include multi-axis machines that permit complex three-dimensional cutting in fewer setups, touch-screen interfaces, and integrated CAM software for streamlined workflows. Appropriate pairing of machine type to material, like lasers for thin metals and plasma for thick conductive metals, maximises output quality and speed.
Complementary Equipment and Alternatives
Workshops often integrate additional tools alongside CNC machines. Water jet cutters enable cold cutting for heat-sensitive materials, preserving their integrity. Manual milling machines accommodate intricate, short-run jobs. Press brakes efficiently bend sheet metals. This complementary and versatile toolkit broadens manufacturing scope and flexibility, supporting diverse project requirements beyond CNC’s primary functions, enabling work with a little bit of everything.
The Evolution and Future of CNC Machining
From early numerical controls to today’s intelligent, multi-axis CNC systems with integrated CAD/CAM, CNC technology has grown remarkably. Modern machines operate with microprocessor-driven motors and advanced controls that boost precision and throughput. Future trends include AI-powered toolpath optimisation, predictive maintenance, and hybrid manufacturing combining subtractive and additive processes. These advancements will further enhance precision, flexibility, and efficiency to meet evolving industrial needs.
Deepening Technical Insights: Specifications and Features
To choose the ideal one, understanding core specifications is vital. Machine configurations vary from basic 3-axis systems, offering motion in X, Y, and Z, to advanced 5 and 6-axis models enabling more complex shapes by rotating the part along additional axes. 5-axis CNC machines allow access to multiple sides of a component without repositioning, improving speed and accuracy, crucial in aerospace and medical sectors.
Some other technical factors include spindle speed and power, which influence cutting effectiveness across materials; table size, defining the maximum workpiece dimensions; feed rates affecting surface finish and cycle times; and control systems, where intuitive interfaces and customisable software post-processors aid programming efficiency and accuracy.
Build quality impacts machine stability and longevity, with durable materials like cast iron or steel often preferred for precision and vibration reduction. Tooling complements specifications; milling cutters, drills, reamers, and taps made from carbide or high-speed steel suit varied machining tasks, affecting cost and output quality.
Design considerations in CNC machining embrace tolerances, hole sizes, radii, text engraving, and surface finish to balance functionality with manufacturing costs. Standards like ISO 2768 guide tolerance levels, aiding consistency. Attention to these details ensures reliable, repeatable production aligned with product requirements.
Embracing Precision with Confidence
Choosing CNC technology that aligns with specific goals and material requirements enhances manufacturing outcomes. Armed with knowledge about machine types, specifications, compatible materials, and maintenance needs, businesses can secure equipment that minimises downtime and maximises quality. A user-friendly, reliable, and upgrade-capable CNC machine forms the foundation of efficient, scalable production.
Thoughtful investment in CNC technology empowers manufacturers to innovate and adapt in a competitive, rapidly evolving industrial world, delivering precision and consistency that meet modern standards and customer expectations.











